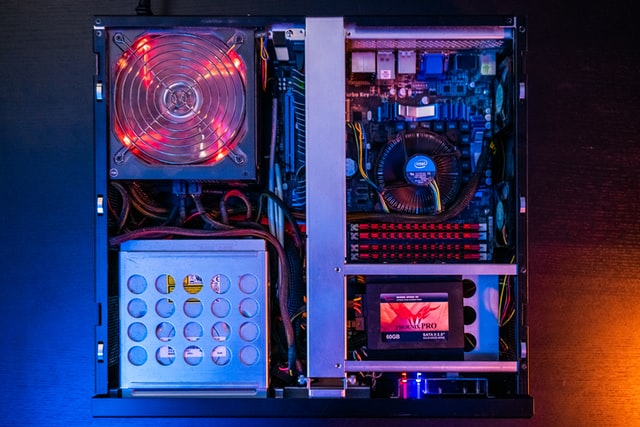
Overclocking, or the act of increasing a computer’s clock speed beyond factory settings, can damage your CPU. However there are certain methods that will not cause any harm to these devices and their users. Before doing so you should ensure your motherboard does not have overclocking enabled as this is one way overclocks can lead to permanent damage.,
The “can overclocking damage gpu” is a question that has been asked for many years. The answer to this question is “it depends!”
Overclocking has been a favorite pastime of PC fans for decades. Since NCIX acquired Linus Tech Tips, I’ve seen him lecture about overclocking. Whether or not you agree with the advantages of overclocking, it has had a significant influence on PC gaming culture.
What, on the other hand, are some of the dangers of contemporary overclocking? Is it possible for your CPU to be fried?
Overclocking your CPU has the potential to destroy it, but newer hardware has far stronger safety safeguards. Today’s motherboards will shut down before a problem with excessive voltage arises, but improper cooling might create major issues. Overclocking has little effect on the longevity of your CPU.
This isn’t true for every CPU on the market. Of course, you should use caution anytime you begin tinkering with your computer’s components. When you overclock, proper cooling, voltage regulation, and system monitoring are all critical.
What Is Overclocking and How Does It Work?
Your CPU provides a signal to the rest of your computer, instructing it to transmit and receive data. This occurs a certain amount of times every second.
This is the Gigahertz frequency (HGx) seen on CPU specifications, often known as the Clock Rate. The basic clock speed of a modern-day CPU is roughly 3.5GHz, or around 3,500,000,000 pulses per second.
However, in the late 1980s, several astute PC fans discovered something unique. The clock speed will improve if they can boost the voltage sent to their CPU. Occasionally, by a significant shift.
Their computer will become much speedier as a result of this. There have even been instances when CPUs have almost doubled in power. People have even taken this concept and run with it, overclocking graphics cards and RAM to get more power out of them.
Is it a good idea to overclock my CPU?
With the passage of time, new updates and technologies are introduced. Overclocking your CPU is nearly a thing of the past nowadays. However, most current CPUs nowadays have clock rates that are approaching their limitations.
The performance difference between these new chipsets, however, is minimal at best. That doesn’t rule out the possibility, since most AMD and Intel CPUs now come unlocked, allowing you to choose.
Today’s processors are already pushed to their limits right out of the box. When compared to some of the modern CPUs that peak out at approximately 4GHz, your maximum speed is just around 5GHz. That’s a 25% gain, but it comes at the expense of increased power usage and PC temperatures.
Youtube has a nice demonstration of the difference between 4GHz and 5GHz. In actuality, you’re barely getting an additional 10-20 frames per second. For all that work, it’s a rather tiny rise.
In the end, I don’t believe it’s worth it. Why bother when you’re currently at 110fps when the eye can’t discern frame increases above 60fps?
What Are the Chances of Overclocking Harming Your CPU?
With today’s technology, the odds of your CPU being damaged are limited to none. However, not only does this come with the chance of harming your CPU, but it also comes with the risk of injuring other components. Most motherboards and CPUs will automatically shut down if there is a danger of significant harm.
The most serious danger of overclocking is that the CPU’s lifetime will be shortened. Overclocking is when you operate your computer at a greater temperature and voltage than it was meant to function at. This implies your transistors may age more quickly as a result of this.
Even while transistors will age with time, this might cut their lifetime by up to a year. However, most CPUs live for 20 years or more, so this isn’t a major concern.
What Kind of Harm Does Overclocking Cause?
So far, we’ve discussed the probabilities, but what about the real harm to your CPU? Is it capable of causing significant harm?
It’s crucial to understand that no two computers, regardless of components, are alike. Even if the computers are built identically, you can’t always have entirely equivalent machines. There is always the possibility of change.
CPU Lifespan Has Been Reduced
Your CPU’s internal components will wear out quicker since you’re using it at greater temperatures. This is a normal process that occurs independently of the increased heat; however, the additional heat will hasten it.
Unfortunately, there isn’t much evidence out there that illustrates how serious this decline may be. It seems that it will take anything from six months to a year to deactivate your CPU, but there isn’t enough information to know for sure.
Damage to Components Due of the extreme heat,
Overclocking makes your computer run hotter, which might lead to major difficulties if cooling isn’t properly regulated. Under load, most CPUs can function at temperatures of 50°C (122°F) to 80°C (176°F).
The ambient temperature in your case will grow if you don’t have a robust cooling system. Other components, like as your graphics card or motherboard, may be harmed as well.
Stuttering and Trustworthiness
You may encounter stuttering and frame loss if your clock speeds or voltage are incorrect. This might be why your system begins to drop frames when you’re stressed.
Adjusting your overclock till you hit the “sweet spot” is the simplest method to monitor this. Stuttering may be avoided by gradually increasing the clock speed from its lowest setting to a comfortable maximum.
How Can I Avoid Overclocking-Related Damage?
Naturally, if you overclock your PC or change it in any way, you must exercise prudence. Overclocking in today’s world is as easy as changing a few BIOS settings. However, you must be vigilant and keep an eye on your temperatures.
You’ll also (probably) invalidate your warranty, so there’s that. If you still want to overclock your PC, there are a few things you need take to ensure a smooth process.
BIOS and Drivers for your Motherboard need be updated.
Naturally, you should double-check that everything is up to date before proceeding. This entails visiting your manufacturer’s website to see if there are any new drivers or updates available. This will ensure that everything is in working order and that no serious concerns develop.
Metrics on your PC should be checked.
You should keep an eye on your PC’s statistics after you’ve got your CPU overclocked and stable. You’ll want to double-check that everything is within acceptable limits. HWiNFO is arguably the simplest tool for monitoring your system’s information, and it’s also free.
Have Enough Air Conditioning
As previously said, you’ll need to keep track of not just your CPU’s temperature but also the ambient temperature. It is critical to have enough cooling in order to avoid system damage. That includes double-checking that all of your case fans are functioning correctly and that your CPU cooler is up to snuff. Check read our post on the Best Low Profile CPU Coolers for Overclocking if you’re not sure what a decent choice is.
Putting It All Together
Although overclocking is becoming less common, it is still a popular pastime among PC enthusiasts. You’re allowed to experiment with increasing the power of your Threadripper or Alder Lake at your own peril. Although it may not have the same effect on today’s chips as it had in the past, some individuals seek for that performance.
While overclocking is unlikely to do major harm to your CPU, it does have the potential to cause additional wear and tear. In the long term, your other components may suffer, and you may face an abrupt shutdown. The simplest method to achieve this is to keep your temperatures under control, which can be done with the help of decent monitoring software.
Associated Issues
Is it Possible for Overclocking to Harm My Computer?
Damage to your PC components is quite tough with today’s technology. You may harm your CPU, GPU, or Motherboard if you work well past the boundaries of your PC’s capabilities.
Is there a limit to how far I can overclock my CPU?
When overclocked, most contemporary processors now reach approximately 5GHz. This is because getting beyond this would need an enormous amount of electricity. Overclocking contests may reach speeds of 5GHz, but only for a brief time. We would require far better cooling technologies to maintain continuous speeds.
How can I prevent overclocking from causing damage to my CPU?
The simplest and most critical element is to ensure that your CPU temperatures remain steady. Whether you have a water-cooled system or an aftermarket fan, your CPU should run between 50 and 80 degrees Fahrenheit (122 and 176 degrees Fahrenheit) when under stress.
Watch This Video-
Overclocking is a process that allows users to increase the clock speed of their computer’s CPU. The “msi afterburner” is a tool that allows users to overclock their CPU. The best way to avoid damage from overclocking is to use software like “msi afterburner“.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can you damage CPU by overclocking?
A:
Overclocking your CPU is risky. It can cause the computer to malfunction in some way or another, and it can also lead towards a potential early death of the machine if you dont know what youre doing.
Does CPU overclocking depend on motherboard?
A: The speed of your CPU is dependent on the motherboard its installed into. If you have a powerful enough processor and a good enough motherboard, overclocking will be very easy.
Can overclocking cause permanent damage?
A: If you overclock your graphics card, the chances of permanent damage are very low. However, overclocking can cause stress on factors such as power supplies and motherboards that may result in a catastrophic failure.
Related Tags
- can overclocking damage cpu
- can overclocking cpu damage gpu
- how to overclock cpu
- can overclocking damage motherboard
- cpu-z